- EQUIPMENT
-
special cranes
-

Garbage Grab Crane
-

Foundry Overhead Crane
-

Explosion-proof Overhead Crane
-

Tongs Overhead Crane
-

Overhead Crane with Carrier-beam
-

Electromagnetic Overhead Cranes
-

Diesel Hydraulic Straddle Carrier: Flexible Operation and Affordable Solution for Container Handling
-

Upper Spillway Gate Gantry Crane: Reliable Solution for Dam Gate Hoisting and Hydropower Station Operations
-

Harbour Portal Crane: Powerful and Intelligent Solutions for Efficient Port Handling
-

Coke Pot Crane for CDQ: Exceptional Heavy-Duty Red-Hot Coke Handling
-

Emergency Rescue Specialized Crane for Water-Rescue Simulation: Engineered for Lifesaving Training
-

Intelligent Grab Bucket Overhead Crane: Powerful, Precise and Unmanned Bulk Material Handling Solution
-
-
Industry Crane
-

Industry Crane
-

Tundish Cranes
-

Slab Cranes
-

Scrap Cranes
-

Billet Cranes
-

Coil,Bar and Plate Handling Cranes
-

Cement And Precast Crane
-

Power Station Crane
-

Ladle Cranes
-

Paper Industry Cranes
-

Waste to Energy Cranes and Biomass Cranes
-

Tailored Overhead Cranes for Aerospace: High Precision, Efficience, Safety and Reliability
-

Anode Baking Multifunctional Cranes: Versatile, High-Temp Resistant & Smart-Controlled Must-Have for Electrolytic Aluminum Industry
-

Multifunctional Crane For Electrolytic Aluminum: Fulfills All Aluminum Electrolysis Processes, Boosts Plant Efficiency
-

Warehouse Stacker Crane for AS/RS: High-Efficiency, Reliable, Fully Automated Storage
-

Slab Handling Overhead Crane: Metallurgical-Grade Crane for Continuous Casting and Slab Yards
-

Anode Carbon Block Stacking Cranes: 6-Layer Stacking, A Lifting Solution for Carbon Plants’ Efficient Transfer
-
-
Hoist & Winch Trolley
-

Casting Electric Wire Rope Hoist
-

European Model Electric Hoist
-

Explosion-proof Electric Hoist
-

Low-headroom Electric Hoist
-

Electric Chain Hoist
-

2 Types Explosion-Proof Electric Chain Hoists for Hazardous Zones: Gas & Dust Protection
-

2 Types Explosion-Proof Electric Wire Rope Hoists for Industrial Safety: Reliable Gas & Dust-Proof Solutions
-

Manual Hoists for Precision Lifting: Explore 3 Proven Types for Power-Free Operation
-

Air Pneumatic Hoists: 4 Specialized Designs for Precision, Safety, and Harsh Environments
-

HC Type Electric Hoist: Heavy-duty Wire Rope Hoist for Factory Heavy Lifting
-
-
CRANE Spreader
-
Crane Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Turning and Side Hung
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Thick Plate
-

Specialized Electromagnet for Lifting Steel Plates
-

Lifting Electromagnets for Lifting Steel Plates
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Heavy Rail and Profiled Steel
-

Lifting Electromagnet for High Speed Wier(Coiled Bar)
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Rebar and Steel Pipe
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Bundled Rebar and Profiled Steel
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Billet, Girder Billet and Slab
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Steel Scraps
-
- Crane Spreader
- Crane Hook
- Crane Lifting Tongs and Clamps
-
Crane Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets
- CRANE PARTS
- Transfer Cart

The Importance of Compliance: Ensuring Crane Wheel Calculation Aligns with Chinese Standards
14 Oct, 2023
Crane is an important engineering machinery for material handling, its application areas are quite wide. Involving people’s production and life, industrial and mining enterprises, national defense construction, aerospace and many other aspects. Crane wheels as its walking mechanism in the implementation of the elements, is to bear the working load of the equipment and realize the key components of the material handling. Therefore, the calculation and selection of crane wheels are crucial to ensure the stability and safety of the machine.
In this paper, we will explain how to determine the working diameter of crane wheels through calculation and verify whether the load carrying capacity of the wheels meets the use requirements and other elements. Key parameters and calculation formulas are covered in the article to help you make the correct calculation and selection in the actual project.
The design, selection and production of wheelsets should meet the requirements of relevant national standards:
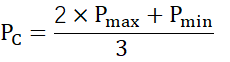 In the formula
PC — wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
Pmax — the maximum wheel pressure during normal operation of the crane (N);
Pmin — the minimum wheel pressure when the crane is working normally (N);
II.The wheel tread contact strength calculation:
Wheel and track contact form attached figure:
In the formula
PC — wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
Pmax — the maximum wheel pressure during normal operation of the crane (N);
Pmin — the minimum wheel pressure when the crane is working normally (N);
II.The wheel tread contact strength calculation:
Wheel and track contact form attached figure:
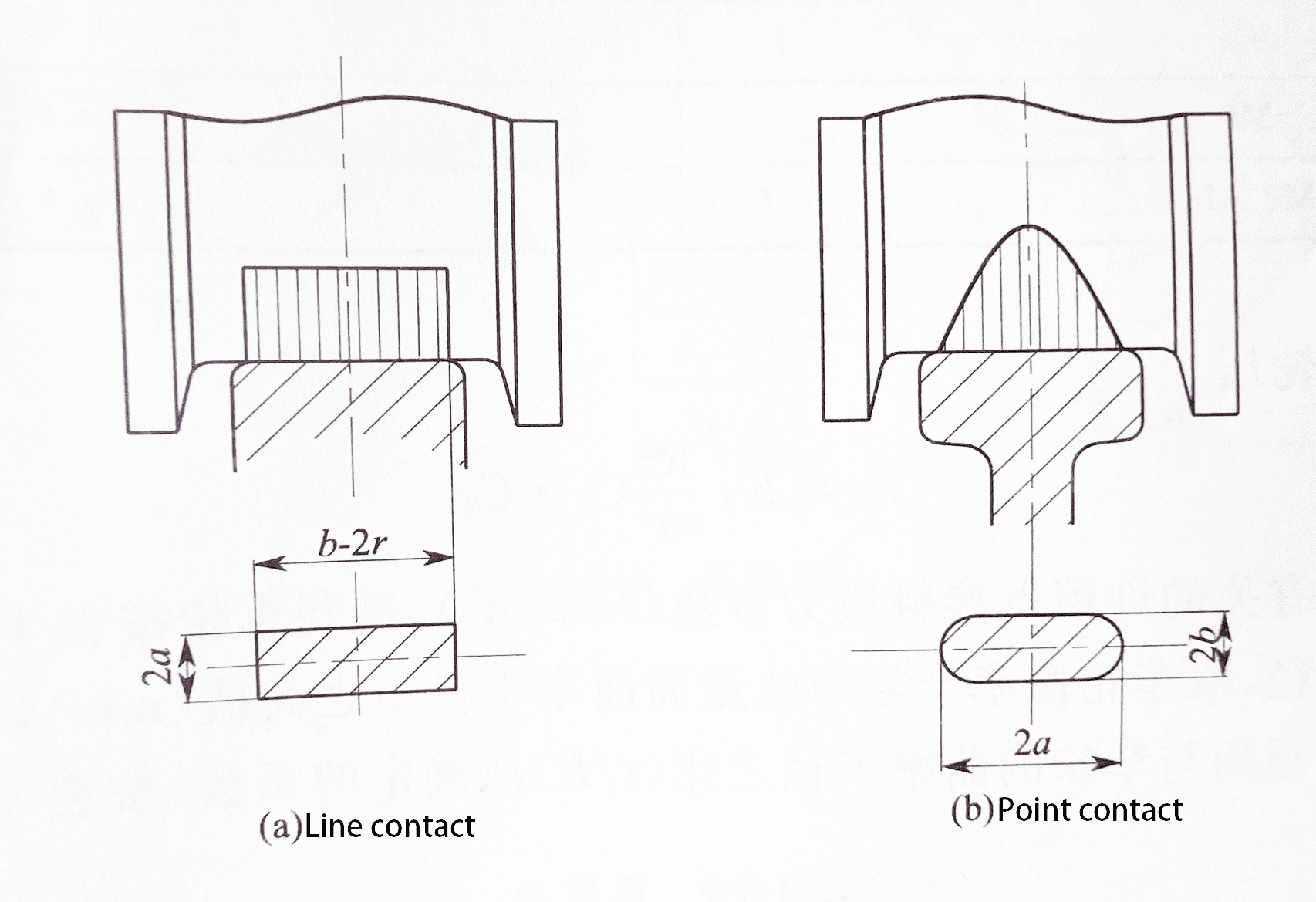 1. Allowable wheel pressure for line contact:
Pc≤K1×D×L×C1×C2
Where
PC —- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K1 —– material-related permissible line contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
D —– wheel diameter (mm);
L—— effective contact length between wheel and rail;
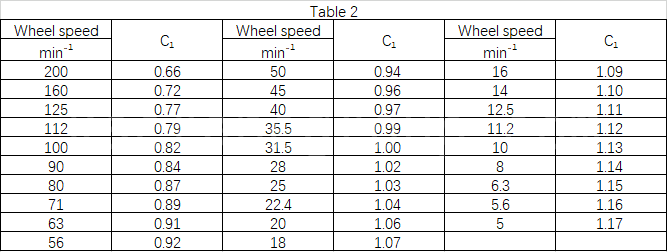
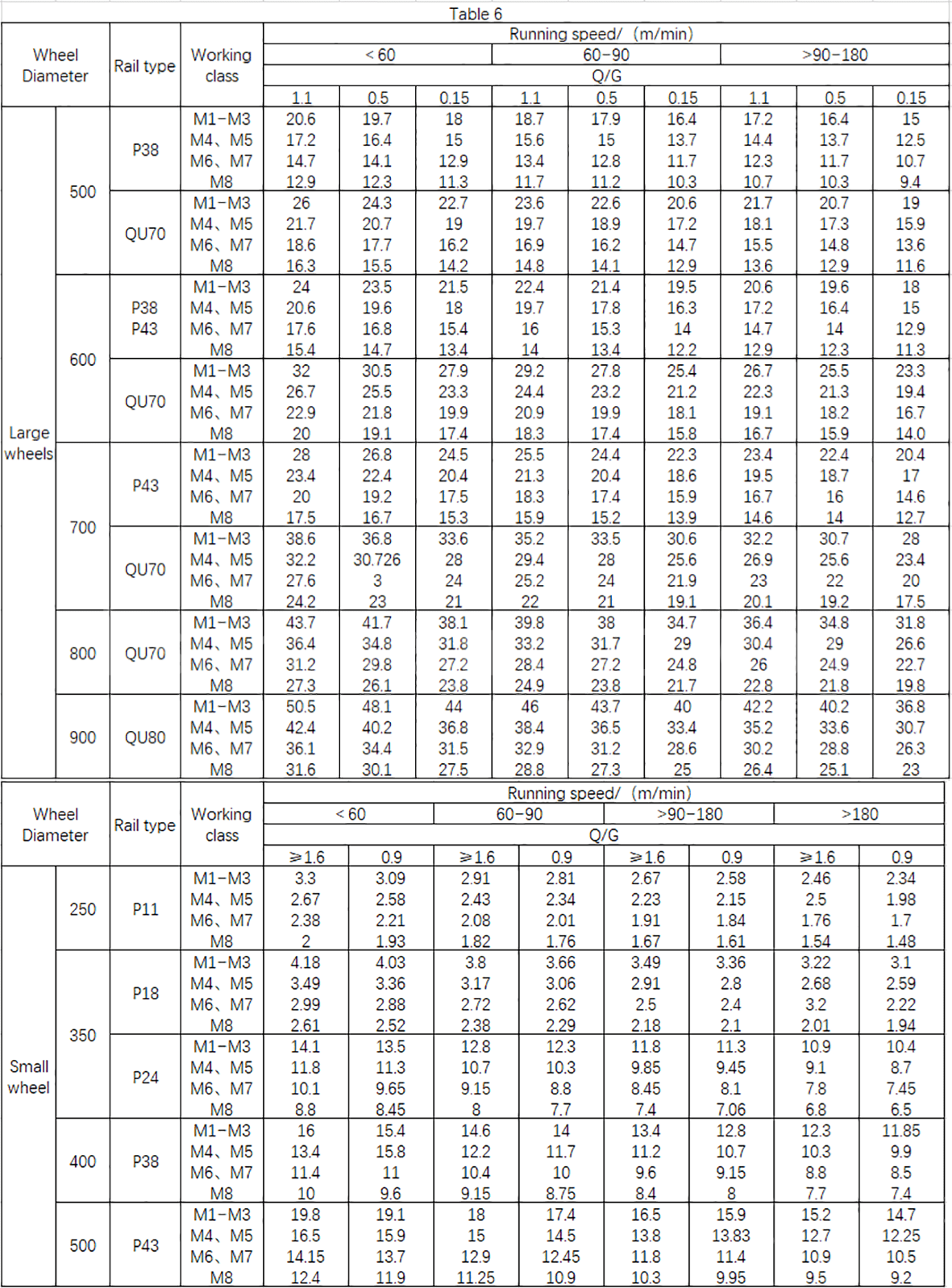
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
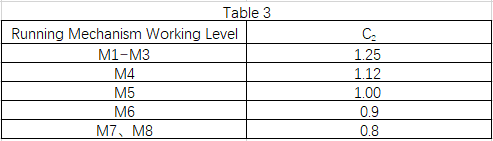
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
2. Allowable wheel pressure for point contact:
1. Allowable wheel pressure for line contact:
Pc≤K1×D×L×C1×C2
Where
PC —- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K1 —– material-related permissible line contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
D —– wheel diameter (mm);
L—— effective contact length between wheel and rail;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
2. Allowable wheel pressure for point contact:
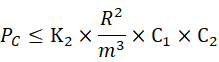 Where
PC—- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K2 —– material-related permissible point contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
R —– curvature radius, take the wheel radius of curvature and track radius of curvature in the larger value (mm);
M—— ratio of the top surface of the track to the radius of curvature of the wheel (r/R), selected according to Table 4;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
Schedule of calculated coefficients:
Where
PC—- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K2 —– material-related permissible point contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
R —– curvature radius, take the wheel radius of curvature and track radius of curvature in the larger value (mm);
M—— ratio of the top surface of the track to the radius of curvature of the wheel (r/R), selected according to Table 4;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
Schedule of calculated coefficients:
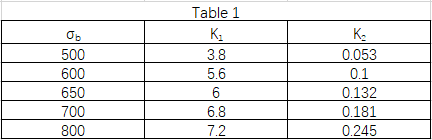 Note:
1. σb is the tensile strength of the material (N/mm2);
2. Steel wheels should generally be heat-treated, tread hardness recommended for HB = 300 ~ 380, quenching layer depth of 15mm ~ 20mm, in determining the permissible value, take the σb when the material is not heat-treated;
3. When the wheel material adopts ductile iron; σb.≥500N/mm2 material, K1, K2 value is selected according to σb.=500N/mm2.
Note:
1. σb is the tensile strength of the material (N/mm2);
2. Steel wheels should generally be heat-treated, tread hardness recommended for HB = 300 ~ 380, quenching layer depth of 15mm ~ 20mm, in determining the permissible value, take the σb when the material is not heat-treated;
3. When the wheel material adopts ductile iron; σb.≥500N/mm2 material, K1, K2 value is selected according to σb.=500N/mm2.
 Note:
1. When r/R is any other value, the m-value is calculated by interpolation;
2. r is the small value of the radius of curvature of the contact surface
The above calculations can be used to verify the verification of the wheels of the set diameter, in order to determine the effective maximum bearing capacity of the wheels and the reasonableness of the dimensions (diameter of the wheels, wheels and rail with the dimensions, etc.).
Note:
1. When r/R is any other value, the m-value is calculated by interpolation;
2. r is the small value of the radius of curvature of the contact surface
The above calculations can be used to verify the verification of the wheels of the set diameter, in order to determine the effective maximum bearing capacity of the wheels and the reasonableness of the dimensions (diameter of the wheels, wheels and rail with the dimensions, etc.).
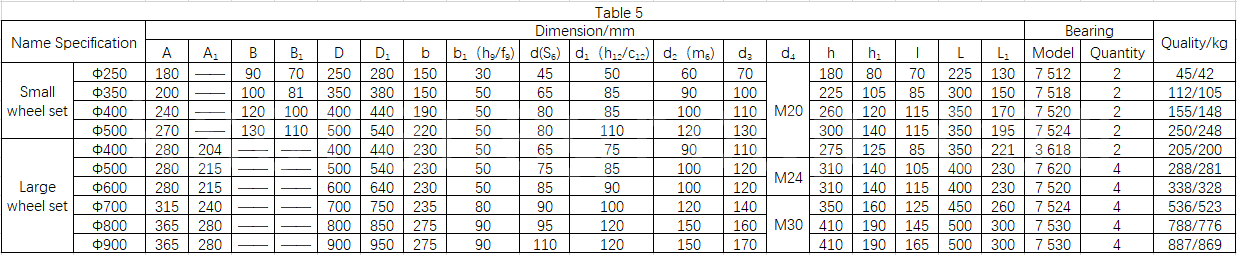
 Crane wheel set series attached chart:
Crane wheel set series attached chart:

- GB/T3811-2008 《Crane Design Code》;
- JB/T6392-2008 《Crane Wheel》;
- YB/T5055-1993 《Crane Rails》;
- GB2585-2007 《Hot Rolled Steel Rails for Railroads》;
- GB/T699-2015 《High Quality Carbon Structural Steel》;
- GB/T11352-2009 《Cast Carbon Steel Parts for General Engineering Purposes》;
- GB/T1184-1996 《Tolerances for Shape and Position, Unannotated Tolerance Values》;
- GB/T1801-1999 《Limits and Fits Selection of Tolerance Zones and Fits》;
The following are the detailed steps for wheel calculation:
- Collect data: First, determine the working load of the crane wheel, track size, wheel and track contact form, institutional working level, walking speed, wheel material, etc.
- Apply the formula: use the formula, these parameters are correctly substituted into the formula.
- Calculation results: According to the data provided and the formula, the wheel is calculated and verified, and whether the result meets the requirements is derived from the calculation results and the judgment conditions in the formula.
Calculation formula of the wheel:
I. Determination of wheel fatigue calculation load: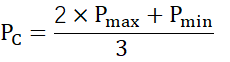 In the formula
PC — wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
Pmax — the maximum wheel pressure during normal operation of the crane (N);
Pmin — the minimum wheel pressure when the crane is working normally (N);
II.The wheel tread contact strength calculation:
Wheel and track contact form attached figure:
In the formula
PC — wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
Pmax — the maximum wheel pressure during normal operation of the crane (N);
Pmin — the minimum wheel pressure when the crane is working normally (N);
II.The wheel tread contact strength calculation:
Wheel and track contact form attached figure:
 1. Allowable wheel pressure for line contact:
Pc≤K1×D×L×C1×C2
Where
PC —- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K1 —– material-related permissible line contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
D —– wheel diameter (mm);
L—— effective contact length between wheel and rail;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
2. Allowable wheel pressure for point contact:
1. Allowable wheel pressure for line contact:
Pc≤K1×D×L×C1×C2
Where
PC —- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K1 —– material-related permissible line contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
D —– wheel diameter (mm);
L—— effective contact length between wheel and rail;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
2. Allowable wheel pressure for point contact:
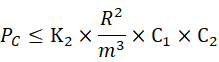 Where
PC—- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K2 —– material-related permissible point contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
R —– curvature radius, take the wheel radius of curvature and track radius of curvature in the larger value (mm);
M—— ratio of the top surface of the track to the radius of curvature of the wheel (r/R), selected according to Table 4;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
Schedule of calculated coefficients:
Where
PC—- wheel fatigue calculation load (N);
K2 —– material-related permissible point contact stress constant (N/mm2), selected according to Table 1;
R —– curvature radius, take the wheel radius of curvature and track radius of curvature in the larger value (mm);
M—— ratio of the top surface of the track to the radius of curvature of the wheel (r/R), selected according to Table 4;
C1—– speed coefficient, selected according to Table 2;
C2—– working level coefficient, selected according to Table 3;
Schedule of calculated coefficients:
 Note:
1. σb is the tensile strength of the material (N/mm2);
2. Steel wheels should generally be heat-treated, tread hardness recommended for HB = 300 ~ 380, quenching layer depth of 15mm ~ 20mm, in determining the permissible value, take the σb when the material is not heat-treated;
3. When the wheel material adopts ductile iron; σb.≥500N/mm2 material, K1, K2 value is selected according to σb.=500N/mm2.
Note:
1. σb is the tensile strength of the material (N/mm2);
2. Steel wheels should generally be heat-treated, tread hardness recommended for HB = 300 ~ 380, quenching layer depth of 15mm ~ 20mm, in determining the permissible value, take the σb when the material is not heat-treated;
3. When the wheel material adopts ductile iron; σb.≥500N/mm2 material, K1, K2 value is selected according to σb.=500N/mm2.


 Note:
1. When r/R is any other value, the m-value is calculated by interpolation;
2. r is the small value of the radius of curvature of the contact surface
The above calculations can be used to verify the verification of the wheels of the set diameter, in order to determine the effective maximum bearing capacity of the wheels and the reasonableness of the dimensions (diameter of the wheels, wheels and rail with the dimensions, etc.).
Note:
1. When r/R is any other value, the m-value is calculated by interpolation;
2. r is the small value of the radius of curvature of the contact surface
The above calculations can be used to verify the verification of the wheels of the set diameter, in order to determine the effective maximum bearing capacity of the wheels and the reasonableness of the dimensions (diameter of the wheels, wheels and rail with the dimensions, etc.).

 Crane wheel set series attached chart:
Crane wheel set series attached chart:

Special types of crane wheel selection
Explosion-proof crane: explosion-proof crane wheel calculation method as above. Selection, according to the different levels of explosion-proof can choose a different surface form of the wheel. Such as when the explosion-proof level of Ⅱ C, the wheel tread and rim part should not be used due to impact, friction and ignition of explosive gas mixtures of copper alloy or other materials manufactured wheels. Generally, when the explosion-proof level is lower than ⅡC, the surface of the wheels should not be specially treated.Important Notes
Please note the following important matters when making wheel selection calculations:- Wheel type: Different types of wheels have different performance characteristics, so make sure to use the parameters of the correct type of wheel for calculation.
- Project requirements: Depending on the specific project requirements and ground conditions, it may be necessary to adjust the crane wheel diameter. Too small a wheel diameter may cause the machine to be unstable, while too large a diameter may increase the height of the machine and limit its range of use.
- Professional consultation: If you are unsure how to obtain the correct parameters or how to perform the calculations, consult a professional engineer or manufacturer who can provide detailed information about your particular crane.
Do you like what we do?Share it




































.png?w=200&h=134)





















